Schematic of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux system as established in
€ 16.00 · 4.5 (102) · In Magazzino
Di uno scrittore di uomini misteriosi

Download scientific diagram | Schematic of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux system as established in E. coli. The blue cylinder represents the TolC exit duct. The green trapezoid with two tails represents two AcrA adaptor proteins. The three red rectangles sans corners represent the AcrB homotrimer transporter protein from publication: Characterizing active transportation mechanisms for free fatty acids and antibiotics in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 | Background Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 is a photosynthetic bacterium that has been genetically modified to produce industrially relevant chemicals, yet efflux mechanisms have not been well elucidated. These photosynthetic organisms live in environments that are often nutrient | Synechocystis, Fatty Acids and Free Will | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
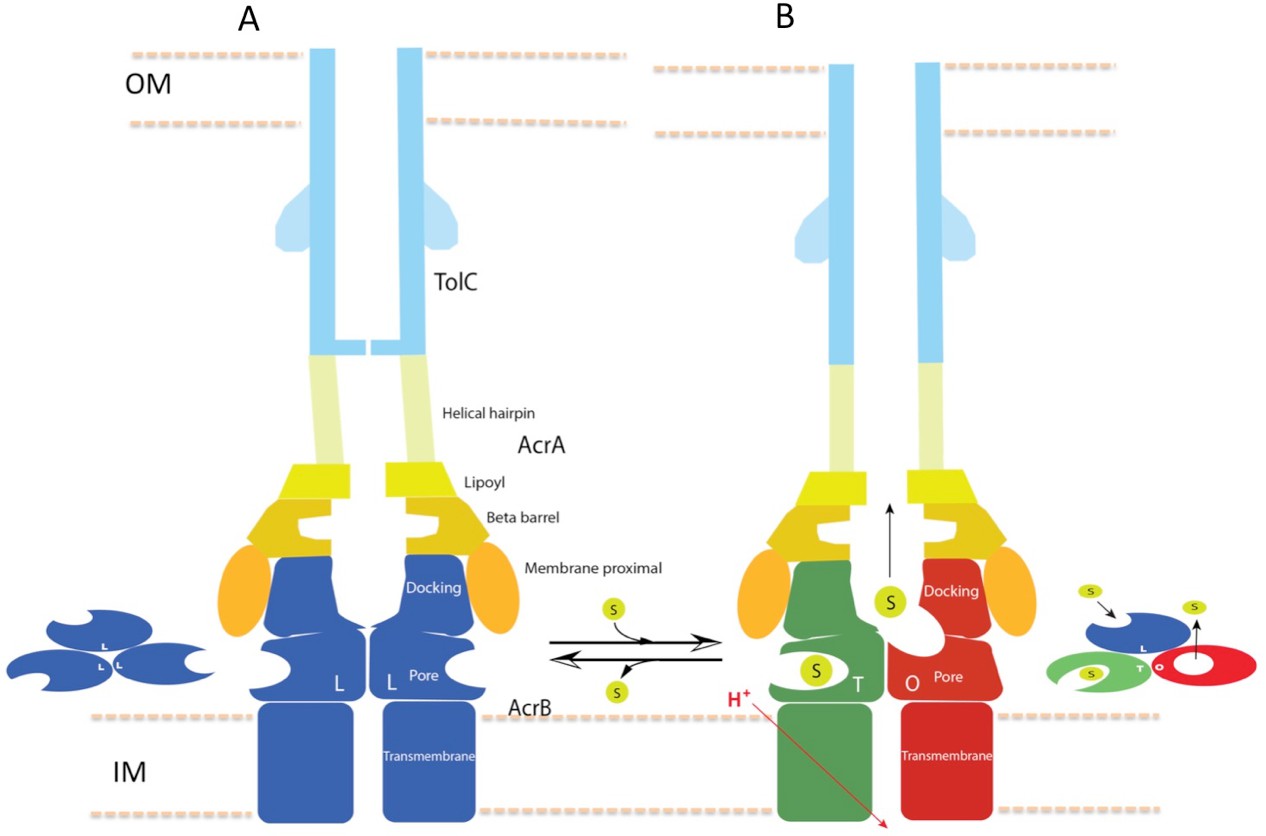
An allosteric transport mechanism for the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump

PDF] Mutations in the TolC Periplasmic Domain Affect Substrate Specificity of the AcrAB-TolC Pump

Model of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump of a Gram-negative bacterium.

Drug transport mechanism of the AcrB efflux pump - ScienceDirect
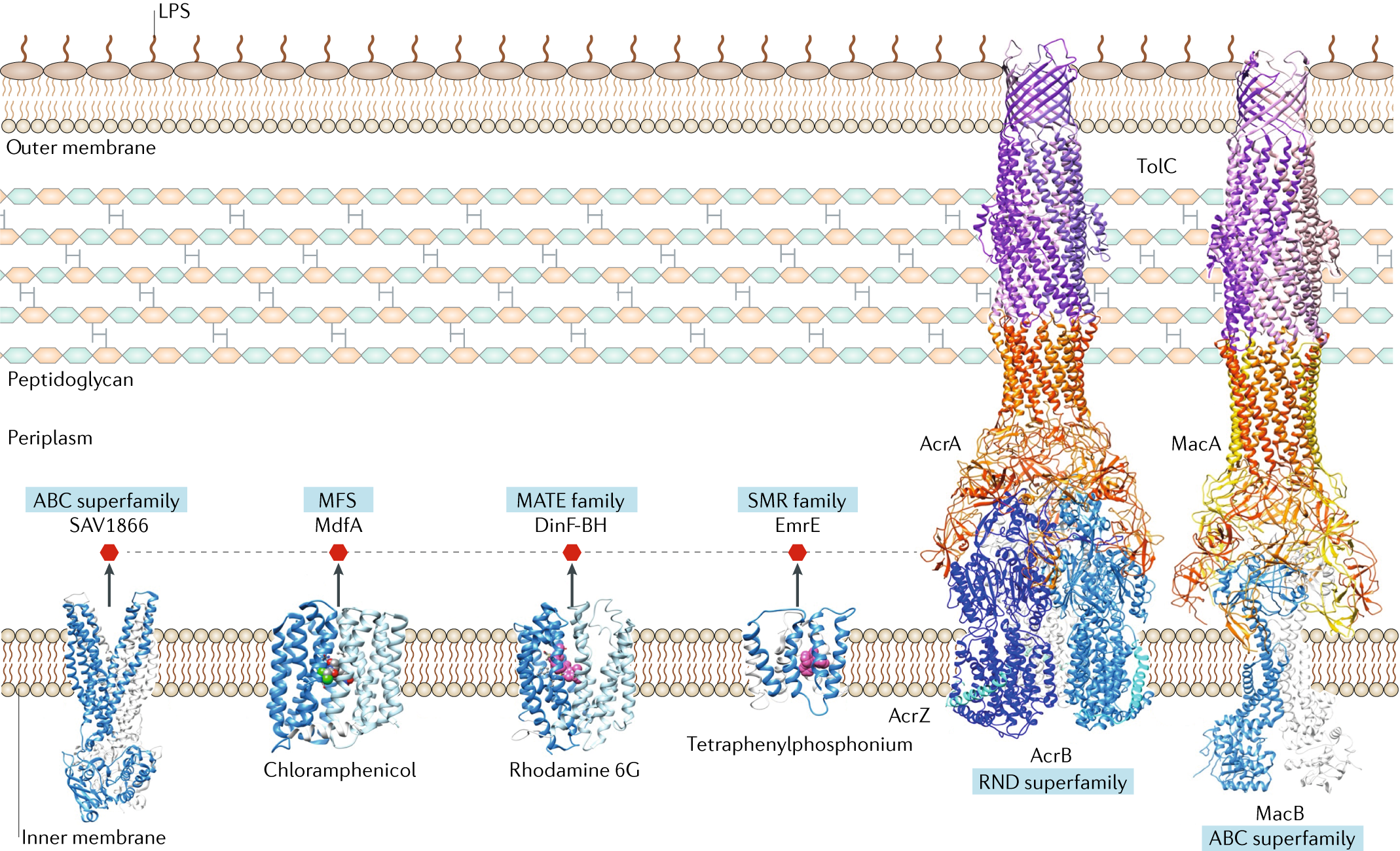
Multidrug efflux pumps: structure, function and regulation

Schematic representation of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump

Structures of the proteins constituting the tripartite AcrAB-TolC

In situ structure of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump at subnanometer resolution - ScienceDirect
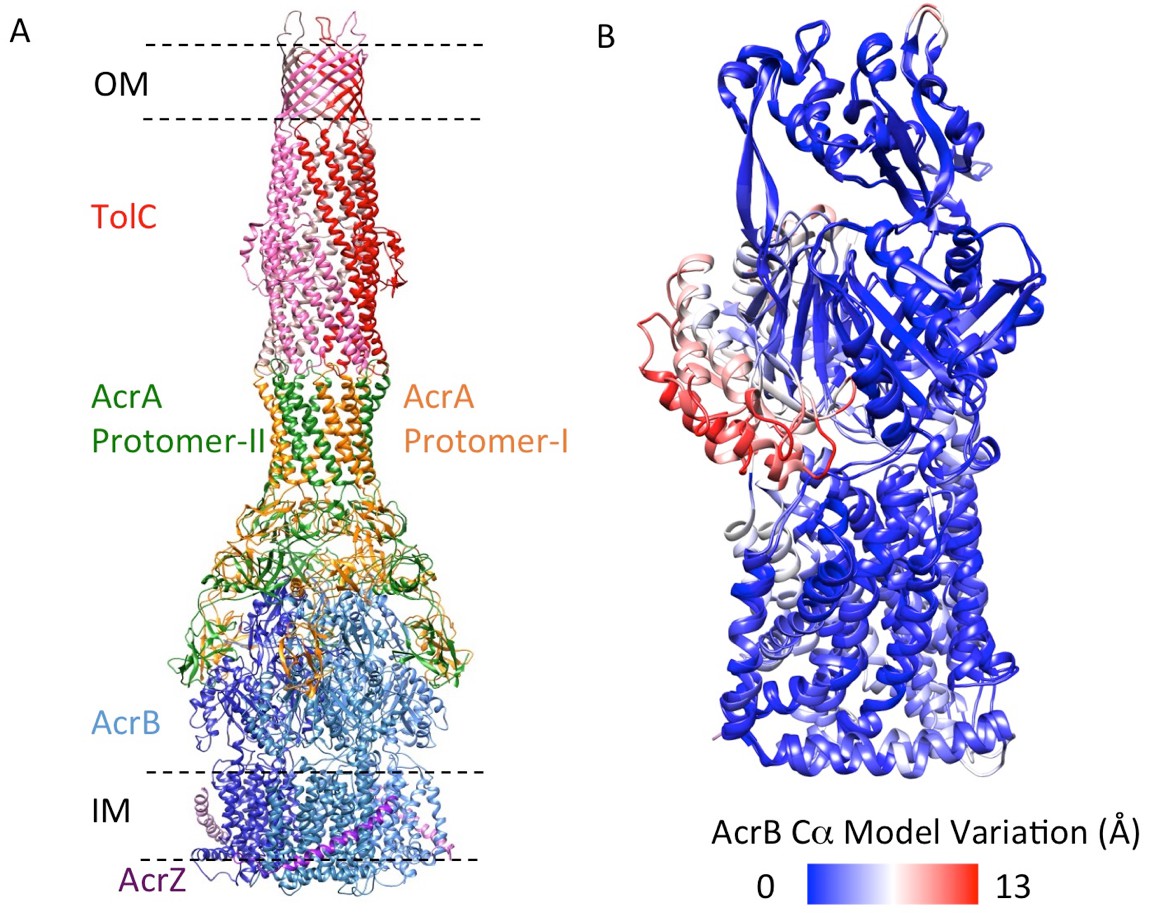
An allosteric transport mechanism for the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump

Figure 1 from RND multidrug efflux pumps: what are they good for?

Assembly and Channel Opening in a Bacterial Drug Efflux Machine: Molecular Cell