The Human Cytomegalovirus Strain DB Activates Oncogenic Pathways in Mammary Epithelial Cells - eBioMedicine
€ 27.99 · 4.7 (285) · In Magazzino
Di uno scrittore di uomini misteriosi


The Human Cytomegalovirus Strain DB Activates Oncogenic Pathways in Mammary Epithelial Cells

Polyploid giant cancer cells, cytokines and cytomegalovirus in breast cancer progression, Cancer Cell International

Human Cytomegalovirus Induces Significant Structural and Functional Changes in Terminally Differentiated Human Cortical Neurons

Frontiers Distinct Oncogenic Transcriptomes in Human Mammary Epithelial Cells Infected With Cytomegalovirus
Frontiers Distinct Oncogenic Transcriptomes in Human Mammary Epithelial Cells Infected With Cytomegalovirus

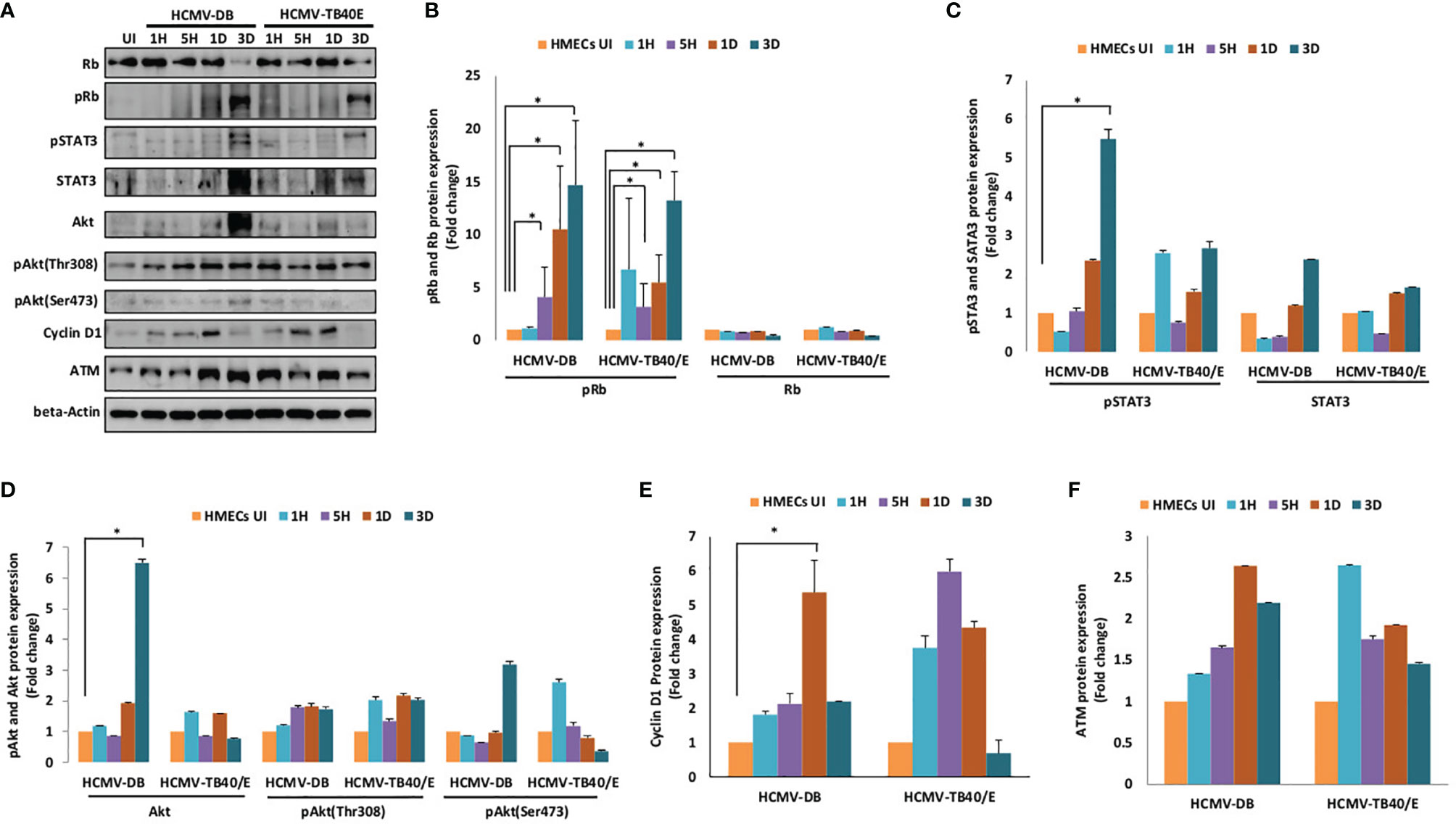
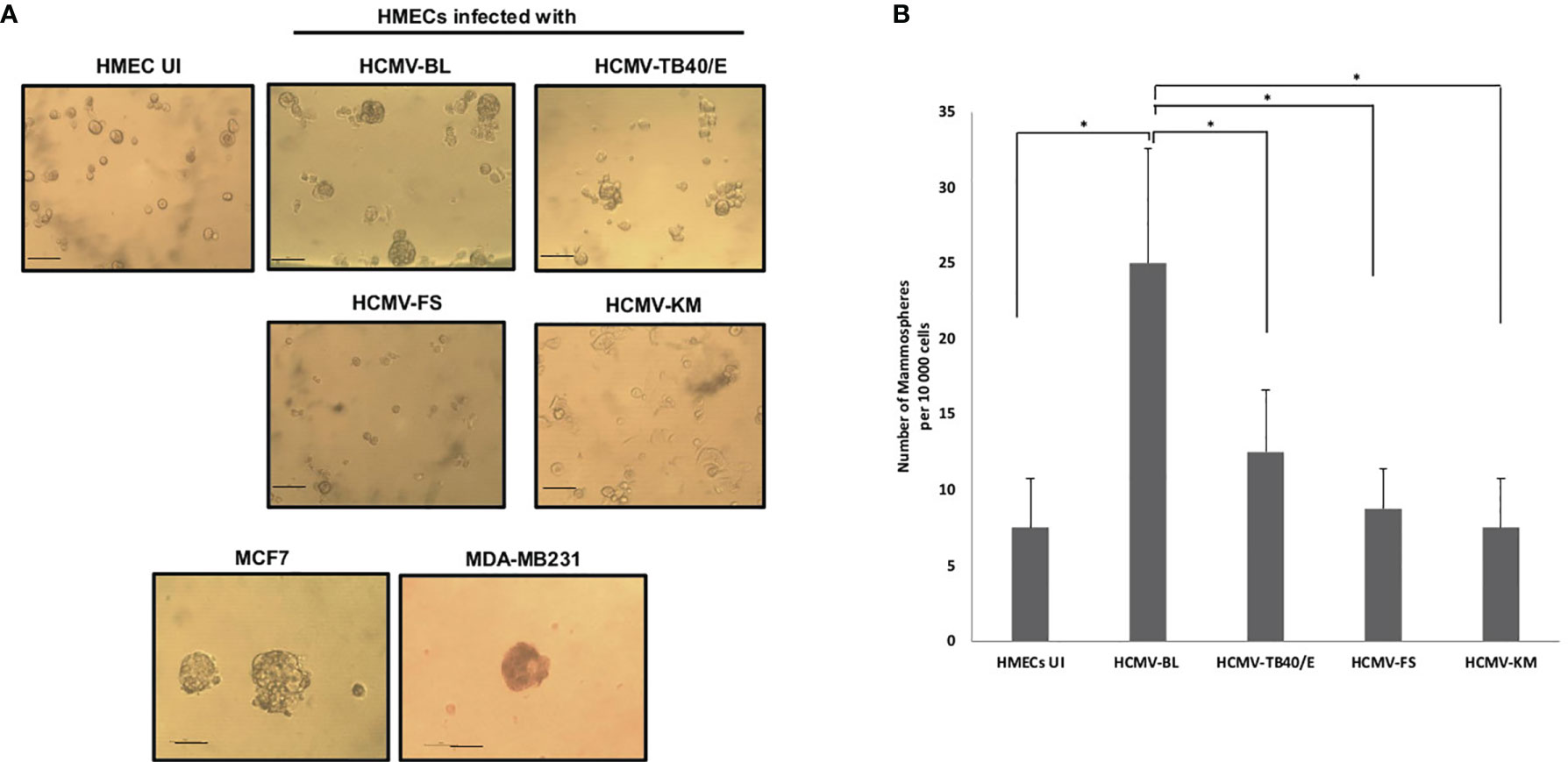
The transcriptome of human mammary epithelial cells infected with the HCMV-DB strain displays oncogenic traits
Frontiers Distinct Oncogenic Transcriptomes in Human Mammary Epithelial Cells Infected With Cytomegalovirus

The Human Cytomegalovirus Strain DB Activates Oncogenic Pathways in Mammary Epithelial Cells - ScienceDirect

Uncovering the Anticancer Potential of Murine Cytomegalovirus against Human Colon Cancer Cells: Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics

Viral G Protein–Coupled Receptors: Attractive Targets for Herpesvirus-Associated Diseases

The transcriptome of human mammary epithelial cells infected with the HCMV-DB strain displays oncogenic traits

Human Cytomegalovirus Induces Significant Structural and Functional Changes in Terminally Differentiated Human Cortical Neurons

Human cytomegalovirus induces significant structural and functional changes in terminally differentiated human cortical neurons
Virus-Induced Oncogenesis

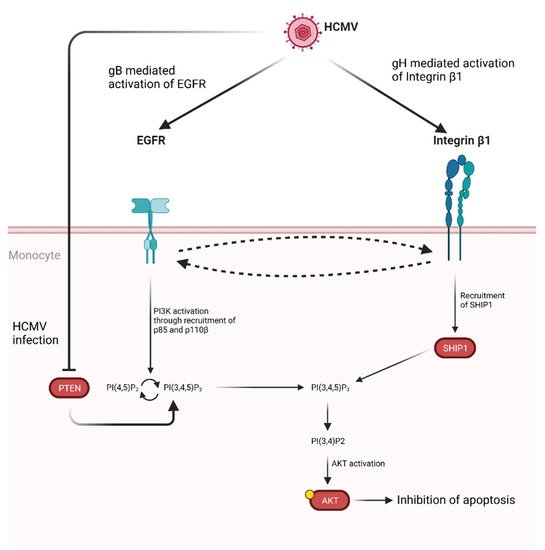
Mechanisms of human cytomegalovirus infection with a focus on epidermal growth factor receptor interactions - Falcão - 2017 - Reviews in Medical Virology - Wiley Online Library